The word trigonometry is the combination of two Greek words Trigon meaning triangle and metron meaning measure. The term trigonometry means measuring the sides of a triangle. Trigonometry was developed to solve geometric problems involving triangles. Trigonometry was studied by sea captains for navigation and surveyors to study the lands. Trigonometry has its applications in various fields like electronics, oceanography, analyzing musical tone, astronomy, and many other areas. In Trigonometry, different types of problems can be solved using trigonometry formulas. Subject experts of Fliplearn have explained each formula with examples in such a way that the student will love to read it and understand the concepts.
There are basically 6 ratios used for finding the elements in Trigonometry. sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, cosecant, and secant are called Trigonometric Functions that defines the relationship between the sides and angles of the triangle.
Trigonometric functions or identities are derived:
The reciprocal relationship between different Trigonometric Functions are as under:
The reciprocal trigonometric identities are also derived by using the trigonometric functions.
Trigonometry table is a table that you can refer to for the values of trigonometric ratios of different angles. To solving problems use the below table for trigonometry formulas for angles:
| Angles (In Degrees) | 0° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° | 180° | 270° | 360° |
| Angles (In Radians) | 0° | π/6 | π/4 | π/3 | π/2 | π | 3π/2 | 2π |
| sin | 0 | 1/2 | 1/√2 | √3/2 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 0 |
| cos | 1 | √3/2 | 1/√2 | 1/2 | 0 | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| tan | 0 | 1/√3 | 1 | √3 | ∞ | 0 | ∞ | 0 |
| cot | ∞ | √3 | 1 | 1/√3 | 0 | ∞ | 0 | ∞ |
| csc | ∞ | 2 | √2 | 2/√3 | 1 | ∞ | -1 | ∞ |
| sec | 1 | 2/√3 | √2 | 2 | ∞ | -1 | ∞ | 1 |
These formulas are used to shift the angles by π/2, π, 2π, etc. They are also called co-function identities.
The co-function or periodic identities can also be represented in degrees as:

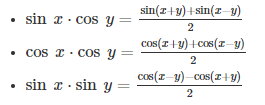
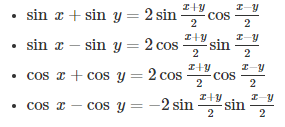
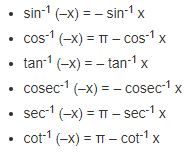
There are six trigonometric ratios. Those are Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cotangent, Secant and Cosecant.
Three main functions in trigonometry are Sin, Cos, and Tan.
Fundamental trigonometry identities are
Schools Say “Hi” to us